Multi-Spindle Systems for Mass Production: Advantages and Challenges
Multi-Spindle Systems for Mass Production: Advantages and Challenges
Modern metalworking has reached a new level of efficiency thanks to innovative technologies. Among them, multi-spindle systems have become a key solution for optimizing mass production. These machines can process several parts simultaneously or perform multiple operations in one cycle, drastically reducing production time and increasing throughput.
This article explores what multi-spindle systems are, their benefits, and the challenges manufacturers face when implementing them.
What Are Multi-Spindle Systems?
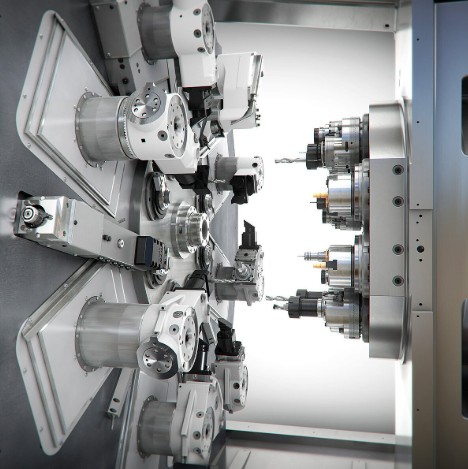
A multi-spindle system is a machine equipped with several spindles that operate simultaneously. Each spindle performs a specific operation, allowing multiple parts to be machined at once or enabling complex processing on a single workpiece without retooling.
Types of Multi-Spindle Systems
-
Parallel systems: multiple spindles operate simultaneously, performing identical or complementary operations.
-
Sequential systems: spindles work in a programmed sequence, maintaining continuous part flow.
-
Combined systems: integrate both approaches for flexible, task-specific optimization.
These systems are common in automotive, aerospace, and electrical engineering industries, where high throughput and consistent quality are essential.
Advantages of Multi-Spindle Systems
1. Increased Productivity
A machine with four spindles can process four parts at once, cutting the production cycle time nearly fourfold compared to single-spindle setups — a critical advantage in mass production.
2. Reduced Labor Costs
Automation allows one operator to supervise multiple spindles simultaneously, minimizing human error and reducing workforce expenses.
3. Faster Changeovers
Automated tool and part changes reduce downtime between batches, maximizing uptime and efficiency.
4. Consistent Quality
Simultaneous processing ensures identical cutting conditions, resulting in uniform part geometry and surface finish, reducing scrap and rework.
5. Optimized Floor Space
A single multi-spindle machine can replace several single-spindle setups, saving valuable floor space and simplifying logistics.
Challenges in Implementing Multi-Spindle Systems
1. High Equipment Costs
Multi-spindle machines are significantly more expensive, and their ROI is achieved only in high-volume production environments.
2. Complex Setup and Programming
Each spindle requires individual cutting parameters. Programming demands highly skilled technicians and precise synchronization.
3. Increased Maintenance Requirements
More spindles mean more moving components, which require consistent preventive maintenance to avoid system-wide downtime.
4. Limited Flexibility
Multi-spindle systems are ideal for mass production of identical parts but less suitable for frequent product changes or custom machining.
5. Strict Workpiece Requirements
To maintain high precision and stability, workpieces must meet tight tolerances; any deviations can lead to simultaneous defects across multiple parts.
Implementation Recommendations
-
Evaluate production volumes to justify investment.
-
Calculate ROI considering machine cost, training, and maintenance.
-
Choose the right configuration based on product type and complexity.
-
Automate auxiliary processes like material loading and quality control.
-
Invest in staff training for smooth operation and reliability.
-
Establish preventive maintenance to avoid unplanned downtime.
Practical Applications
Automotive Industry
Used for mass production of fasteners, gears, and small precision parts with minimal error rates.
Electrical Industry
Ideal for simultaneous production of multiple connectors and casings with uniform geometry.
Medical Equipment
Ensures precision and repeatability in manufacturing surgical instruments and implants.
Conclusion
Multi-spindle systems are a powerful tool for optimizing mass production — boosting productivity, reducing labor, and ensuring consistent quality.
However, successful implementation requires careful planning, skilled personnel, and regular maintenance.
For manufacturers aiming to increase efficiency and competitiveness, multi-spindle technology represents a strategic investment that can deliver significant long-term benefits.